Feds looking at whether Amtrak engineer was distracted by trainee, official says
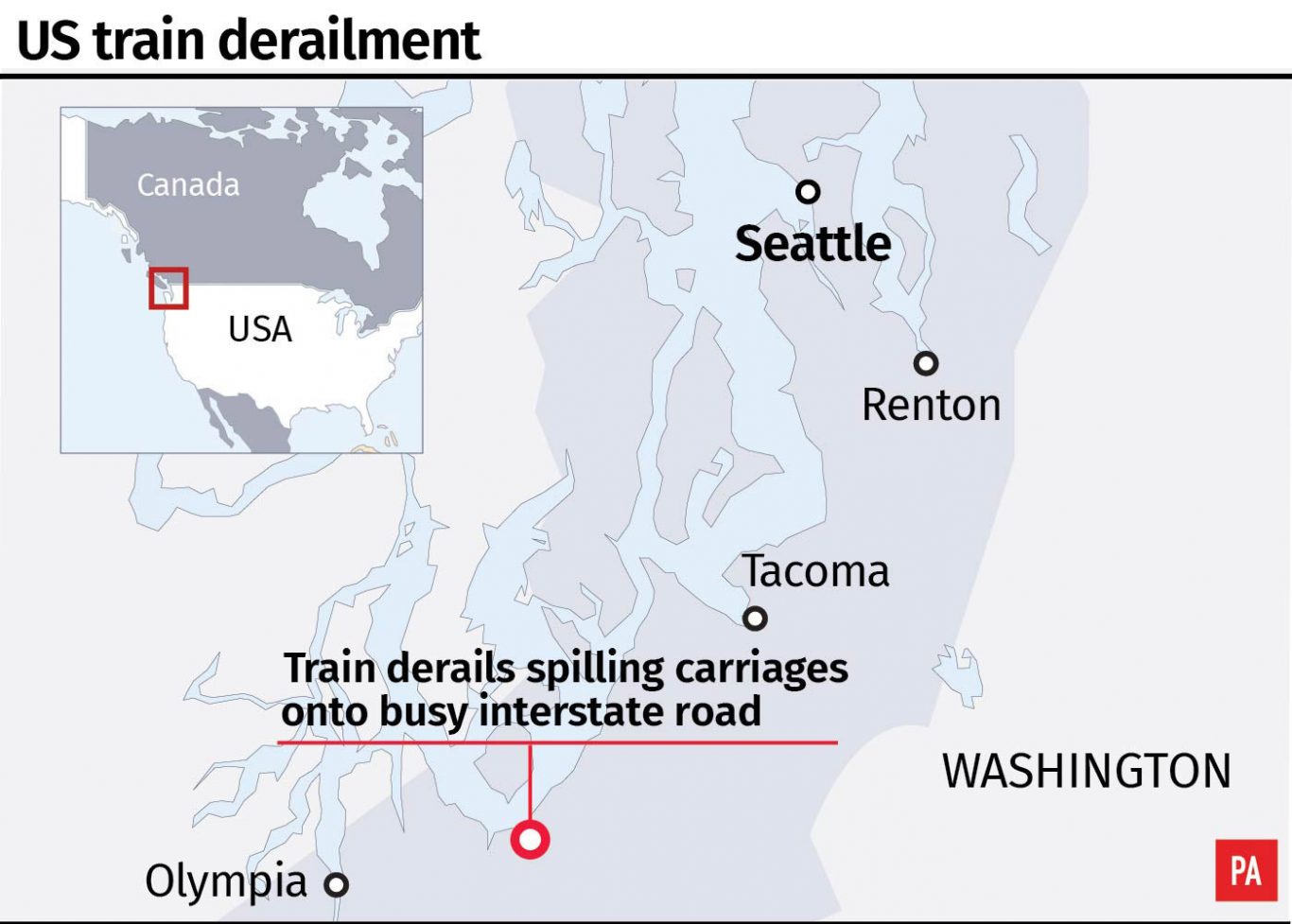
Three people were killed and more than 70 people were treated for injuries after the train derailed near Seattle.

Investigators are looking into whether the Amtrak engineer whose speeding train plunged off an overpass, killing at least three people, was distracted by the presence of an employee-in-training next to him in the locomotive, a federal official says.
The official, who was not authorised to discuss the matter publicly and spoke on condition of anonymity, said investigators want to know whether the engineer lost “situational awareness” because of the second person in the cab.
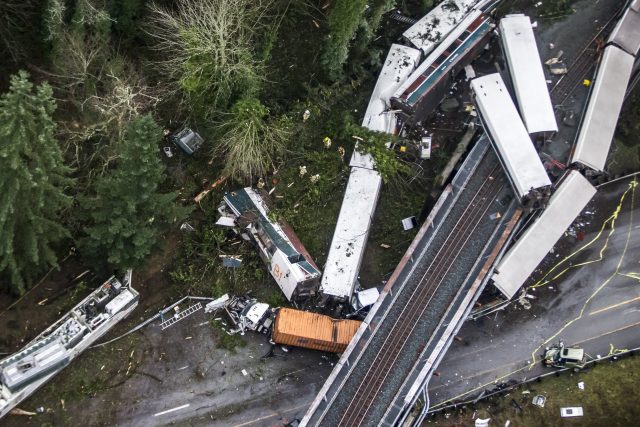
The train was hurtling at 80mph in a 30mph zone on Monday morning when it ran off the rails along a curve south of Seattle, sending some of its cars plummeting onto an interstate highway below, National Transportation Safety Board member Bella Dinh-Zarr said citing data from the locomotive’s event recorder.
In previous wrecks, investigators looked at whether the engineer was distracted or incapacitated.
The engineer, whose name has not been released, was bleeding from the head after the crash and his eyes were swollen shut, according to radio transmissions from a crew member.
The transmissions mentioned a second person in the front of the train who was also hurt.
The train, with 85 passengers and crew members, was making the inaugural run along a fast new bypass route that was created by refurbishing freight tracks alongside Interstate 5.
The 15-mile, 180.7 million dollar project was aimed at speeding up service by bypassing a route with a number of curves, single-track tunnels and freight traffic.
Positive train control — technology that can automatically slow or stop a speeding train — was not in use on that stretch of track.
Track sensors and other PTC components have been installed, but the system is not expected to be completed until the spring, transit officials said.
Regulators have been pressing railroads for years to install such technology, and some have done so, but the deadline has been extended repeatedly at the industry’s request and is now the end of 2018.
The 7.34am accident left mangled train cars up on top of each other, with one hanging precariously over the freeway.
The screech and clang of metal were followed by silence, then screams, as the injured cried out to rescuers and motorists pulled over and rushed to help.
In addition to those killed, more than 70 people were injured, 10 of them seriously.

Two of the dead were identified as train buffs who belonged to the rail advocacy group All Aboard Washington and were excited to be on board for the inaugural run.
They were Jim Hamre, a retired civil engineer with the state Transportation Department, and Zack Willhoite, a customer service employee at a local transit agency.
“It’s pretty devastating. We’re having a tough time,” said All Aboard Washington executive director Lloyd Flem.
In 2015, an Amtrak train travelling at twice the 50mph speed limit ran off the rails along a sharp curve in Philadelphia, killing eight people.
Investigators concluded the engineer was distracted by reports over the radio of another train getting hit by a rock.
In September, a judge threw out charges of involuntary manslaughter and reckless endangerment against the engineer, saying the wreck did not appear to rise to a crime. Prosecutors are trying to get the case reinstated.
In the Washington state crash, speed signs were posted two miles before the speed zone changed, according to Kimberly Reason of Sound Transit, the Seattle-area transit agency that owns the tracks.
After the Philadelphia wreck, Amtrak agreed to pay 265 million dollars to settle claims filed by victims and their families. It has also installed positive train control on all of its track between Boston and Washington.
The NTSB’s Ms Dinh-Zarr said it is too soon to say whether positive train control would have prevented Monday’s tragedy.





