World first GM skin replacement for blister boy
A boy with a life-threatening inherited blistering disease has been given a new coat of genetically modified skin.
A seven-year-old with a devastating inherited disease has been given a new coat of genetically modified skin covering almost the whole of his body.
The pioneering surgery was performed by scientists to save the boy from the life-threatening condition junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB), which causes skin to blister and tear at the slightest touch.
In a world first, the team took a sample of skin just four centimetres square from the child and corrected a disease-causing gene defect within its cells.
The tissue was then grown into grafts that were used to replace 80% of the patient’s skin in three operations.
After 21 months the boy, who had been admitted to a hospital burns unit close to death, appeared to be fully recovered.
His new skin no longer blistered and was able to heal normally.
Returning to his home in Germany, he was able for the first time to enjoy the rough and tumble of a normal schoolboy’s life.
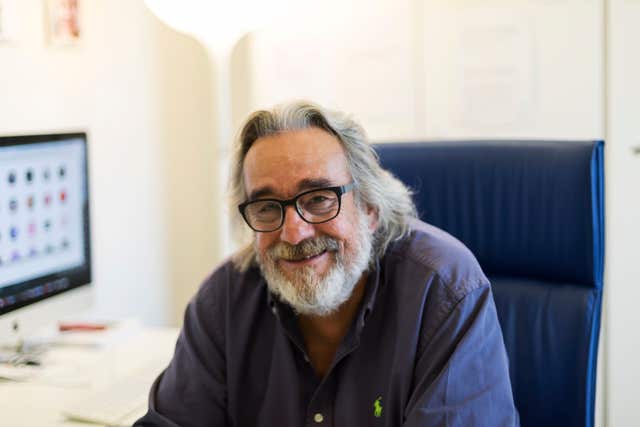

Dr Michele de Luca, from the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Italy, who led the gene therapy team, said: “The patient was in danger of life. The prognosis was very poor, but he survived.
“He went back to normal life, including school and sports. His epidermis is stable; robust. It doesn’t blister at all and functionality is quite good.”
The boy had been transferred to the burns unit at Ruhr-University, Bochum Children’s Hospital in June 2015 with most of his epidermis – the outermost layer of skin – missing or horribly damaged.
All forms of standard treatment proved hopeless, and the child’s body rejected grafts taken from his father.
In desperation doctors contacted experts in other countries, eventually getting in touch with Dr de Luca who was investigating experimental skin regeneration treatments.
The Italian scientists used a virus to insert a healthy version of the rogue Lamb3 gene into cells taken from the skin tissue sample.
These were used to create sheets of genetically modified tissue free from the terrible gene mutation that causes JEB.
Over the course of three operations surgeons attached the new skin grafts to the boy’s body. Once established, the regenerated epidermis maintained itself.
Details of the treatment, previously only used to reconstruct small areas of skin in two patients, appear in the latest issue of Nature journal.
Plastic surgeon Professor Tobias Hirsch, from Bochum Children’s Hospital, described the critical condition of the boy when he was admitted to the burns unit.
Now the boy had “good quality” skin that was “perfectly smooth and quite stable” and required no treatment with special ointments.
Prof Hirsch added: “If he gets any bruises they just heal as normal skin heals.”
He said the child was using a home trainer and playing football.
Treating the boy had provided useful scientific information that improved understanding of how skin was regenerated and maintained, said the scientists.
The research showed that the human epidermis is sustained by a small number of long-lived stem cells with a powerful ability to renew themselves.
These were vital to the process that allowed the skin to regenerate itself completely about once every month.
Writing in Nature, the scientists said: “Transgenic epidermal stem cells can regenerate a fully functional epidermis virtually indistinguishable from a normal epidermis.
“The different forms of epidermolysis bullosa affect approximately 500,000 people worldwide. The successful outcome of this study paves the way for gene therapy to treat other types of epidermolysis bullosa and provides a blueprint that can be applied to other stem cell-mediated ex-vivo (outside the body) cell and gene therapies.”